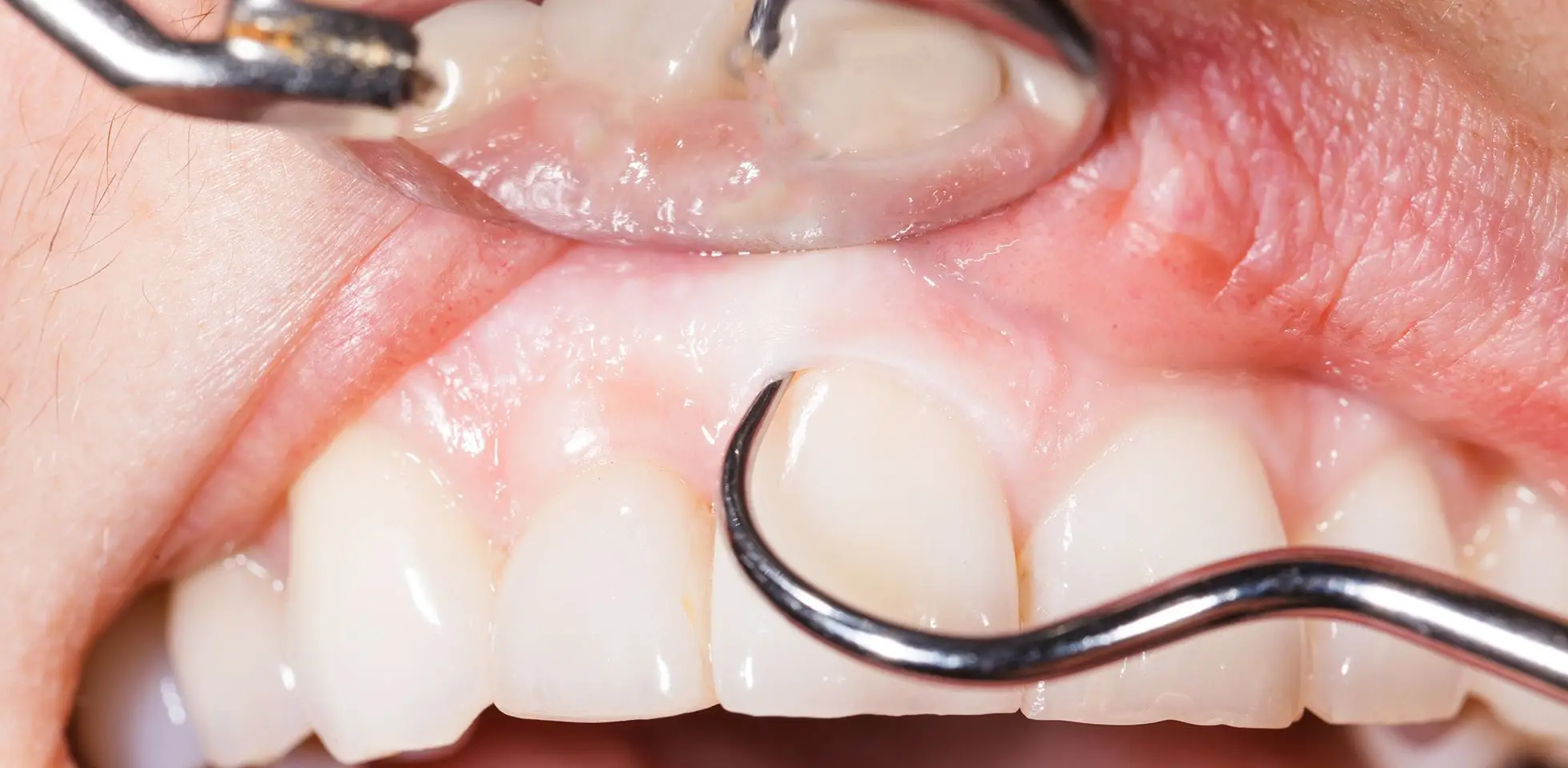
Introduction
Oral Medicine Diagnosis pathology & Radiology is the specialty that focuses on the diagnosis and medical management of diseases of the Head and Neck. It is a unique field of dentistry that combines both Oral Medicine and Craniofacial Radiology.
The Department emphasizes the responsibility of the dentist to see problems affecting the oral region in the context of overall health status
Oral pathology and oral medicine is concerned with the health of the mouth and the diagnosis and management of diseases of the oral region.
Who are the candidates of Oral Medicine and Pathology treatment?
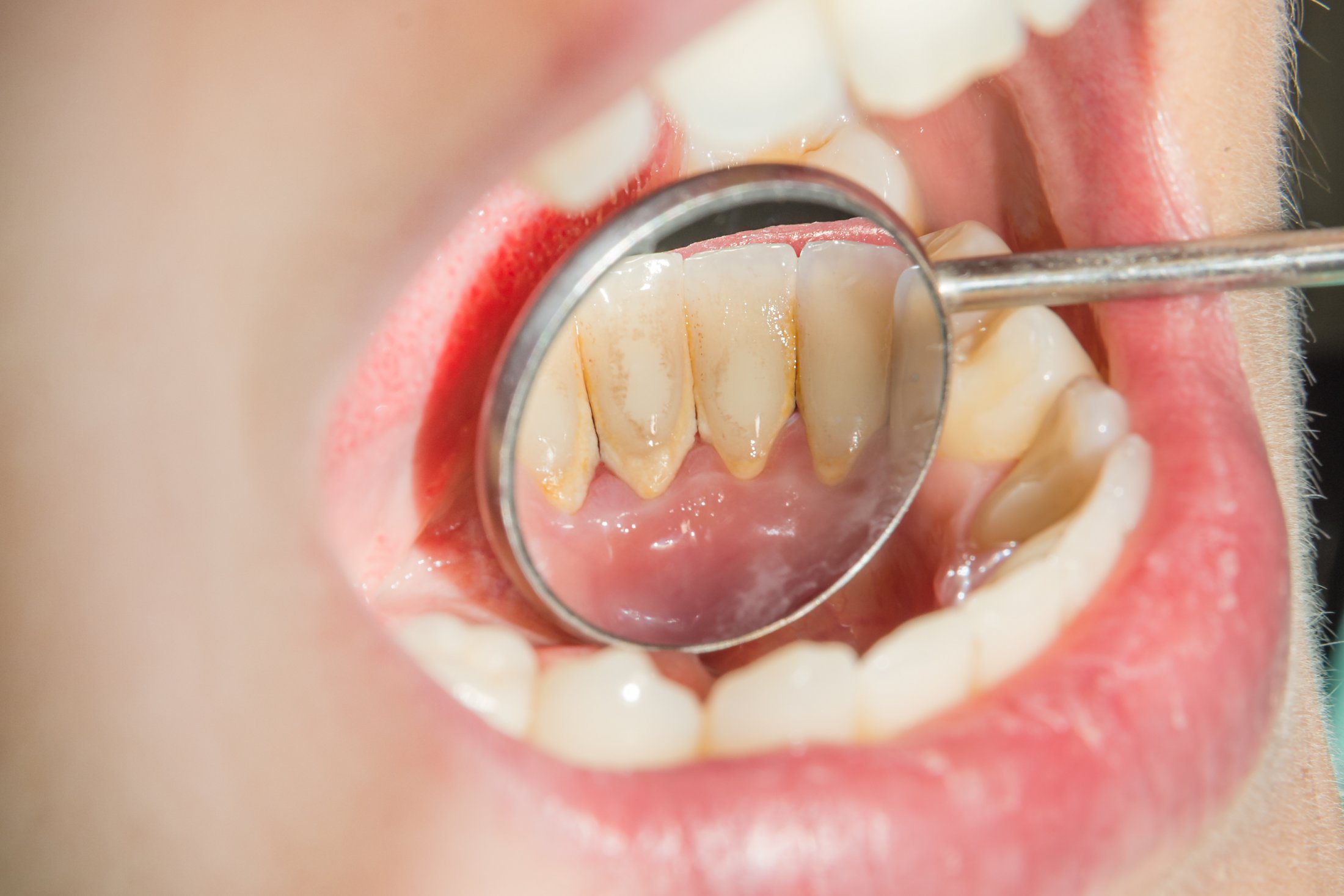
What steps are followed in Oral Medicine and Pathology treatment?
In Oral Medicine and Pathology treatment, the following steps are typically followed:
-
Medical History and Examination:
1 The first step involves taking a detailed medical history and conducting a thorough oral examination. This includes assessing the patient's general health, previous medical conditions, and any medications they are taking. -
Diagnostic Tests:
2 Depending on the symptoms and findings from the examination, the oral medicine specialist may order specific diagnostic tests such as biopsies, imaging studies (X-rays, CT scans), or blood tests to aid in the diagnosis. -
Diagnosis:
3 Based on the patient's medical history, clinical examination, and diagnostic test results, a definitive diagnosis is made. This is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment plan. -
Treatment Planning:
4 The oral medicine specialist devises a treatment plan tailored to the patient's condition. This may involve managing systemic conditions that affect the oral cavity or addressing specific oral diseases. -
Non-surgical Management:
5 In many cases, oral medicine treatment involves non-surgical management, such as prescribing medications, mouthwashes, or topical agents to alleviate symptoms or control oral diseases. -
Patient Education:
6 The specialist educates the patient about their condition, the treatment plan, and preventive measures they can take to maintain oral health. -
Follow-up and Monitoring:
7 Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to assess the patient's response to treatment and make any necessary adjustments. -
Referral:
8 If the oral medicine specialist identifies conditions that require more specialized care or surgical intervention, they may refer the patient to an appropriate specialist, such as an oral surgeon or periodontist. -
Oral Cancer Screening:
9 Routine oral cancer screenings are often conducted, especially for patients at higher risk, to detect any signs of oral cancer early on. -
Oral Health Maintenance:
10 After treatment, patients are encouraged to maintain good oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups to prevent future oral health issues.
What are the advantages of Oral Medicine and Pathology?
Oral Medicine and Pathology treatment offer several advantages for patients. Here are some key benefits:
-
Comprehensive Diagnosis:
1 Oral Medicine and Pathology specialists are trained to provide a thorough and accurate diagnosis of oral diseases and conditions. They have in-depth knowledge of various oral pathologies and can identify the underlying causes of oral symptoms, such as ulcers, lumps, or abnormal tissue changes. -
Multidisciplinary Approach:
2 Oral Medicine and Pathology practitioners often collaborate with other dental and medical specialists, including oral surgeons, periodontists, and oncologists. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that patients receive well-rounded care and appropriate treatment plans tailored to their specific needs. -
Management of Oral Lesions:
3 Oral Medicine and Pathology experts are skilled in managing a wide range of oral lesions, including oral ulcers, mucosal diseases, oral manifestations of systemic diseases, and potentially malignant disorders. They can provide effective treatment options, including topical medications, systemic therapies, or referrals for surgical intervention when necessary. -
Oral Cancer Detection:
4 Early detection is crucial for the successful treatment of oral cancer. Oral Medicine and Pathology specialists are trained to recognize the signs and symptoms of oral cancer and can perform thorough oral cancer screenings. Regular screenings can lead to early detection and improved outcomes. -
Patient Education:
5 Oral Medicine and Pathology practitioners play an essential role in educating patients about oral health, disease prevention, and self-examination techniques. They can provide guidance on maintaining proper oral hygiene, recognizing oral abnormalities, and making lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of oral diseases. -
Research and Advancements:
6 Oral Medicine and Pathology is a field that actively contributes to scientific research and advancements in oral healthcare. Specialists in this field are often involved in clinical trials, studies, and publications, leading to improved diagnostic techniques, treatment modalities, and better patient care overall.
Copyright © Kirthika Dental Care Is Proudly Owned by Macincode
